History
The Bachelor of Science Program in Applied Mathematics (App-Maths) was established in 1989 and revised every five years to be modern, consistent, and relevant to current and future conditions. In 2017, the App-Maths program, the Program Learning Outcomes (PLOs), was mainly based on the Thai Qualifications Framework for Higher Education (TQF: Hed). Subsequently, the ELOs are presented in five domains: (1) morals and ethics, (2) knowledge, (3) intellectual skills, (4) interpersonal skills and responsibility skills, and (5) numerically analytical, communication, and information technology, as shown in Table 1.
In the 2021 revision, the program’s name was changed to Mathematics and Computer Science (MCS), which aims to produce graduates with knowledge in mathematics, statistics, and computer science. To integrate knowledge from all three sciences to apply to solve environmental problems, problems of natural disasters, and unrest in the southern border provinces, as well as create innovations for the sustained development of organizations, communities, and society in the South. The program produces graduates according to the progressivism approach, which is to develop students in every aspect so that they are ready to live happily in society and adapt well to changing situations. Various methods of learning, including problem-based learning and project-based learning, have been implemented in the classroom and the workplace. The learner will be developed through the problem-solving process and self-learning. Develop communication skills, select appropriate technologies, and prepare students to graduate with morality, ethics, honesty, discipline, and competence to follow social norms.
Bachelor of Science (B.Sc.)
Mathematics and Computer Science Program, revised curriculum 2021
B.Sc. (Mathematics and Computer Science)
Philosophy of Education
Philosophy of University Education
Philosophy of the curriculum
The Bachelor of Science Program in Mathematics and Computer Science aims to produce graduates with knowledge in mathematics, statistics, and computer science to integrate the knowledge of all three disciplines to solve environmental problems, natural disasters, and unrest in the southern border provinces and create innovations to sustainably develop organizations, communities, and society in the South. The curriculum produces graduates in line with Progressivism, which is the development of learners in all aspects to be ready to live happily in society and adapt well to changing situations. It uses a variety of learning management processes, emphasizing problem-based learning and project-based learning. There is classroom and workplace practice. Learners are developed through problem-solving and self-learning processes, developing communication skills and selecting appropriate technology, and cultivating learners to be graduates with morality, ethics, honesty, discipline, and compliance with social rules.
The objectives of the program
To organize teaching and learning to produce graduates with the following characteristics:
- Able to think analytically and systematically using mathematical processes
- Have knowledge, understanding, and academic skills in mathematics, statistics, and computer science.
- Integrate knowledge in mathematics, statistics, and computer science to analyze, synthesize, and solve environmental problems, natural disasters, and situations in the three southern border provinces.
- Have teamwork skills, learn by yourself, and communicate using correct and appropriate technology.
- Have morality, ethics, responsibility, honesty, and discipline, and comply with social rules.
Highlights of the program
- The program offers teaching and learning that allows students to integrate knowledge in mathematics, statistics, and computer science.
- The program is equipped with modern tools and teaching methods.
- The faculty in the program has expertise in the field that is recognized both nationally and internationally.
Learning Outcomes of the Course (PLOs)
PLO-1 Prove a given mathematical proposition using logical and reasoning methods.
- Sub PLO1.1 Explain terms and definitions related to a given proposition.
- Sub PLO1.2 Write the structure of a given proposition.
- Sub PLO1.3 Select a method and write a proof using logic and reasoning.
PLO-2 Integrate knowledge of mathematics, statistics, and computers to solve environmental problems, natural disasters, and situations in the three southern border provinces.
- Sub PLO2.1 Analyze problems to determine solutions.
- Sub PLO2.2 Create mathematical or statistical models appropriate to the given problems and situations.
- Sub PLO2.3 Develop a problem-solving method using mathematical methods. Statistics and computers are correct and appropriate.
- Sub PLO2.4 Check the correctness of the results obtained from problem solving.
PLO-3 Develop application programs according to user needs and in accordance with development procedures.
- Sub PLO3.1 Analyze problems to determine user needs and system needs.
- Sub PLO3.2 Design program procedures and data structures.
- Sub PLO3.3 Write a set of instructions to make the program and data structures work as designed.
- Sub PLO3.4 Test the correctness of the program and fix the program.
- Sub PLO3.5 Write program documentation.
PLO-4 Work with others as a good leader and member. and adapt to the situation appropriately
PLO-5 Communicate effectively and appropriately according to the situation.
PLO-6 Learn by yourself and keep up with technology.
- Sub PLO6.1 Research and seek knowledge from reliable sources
- Sub PLO6.2 Be aware of changes in knowledge in related fields
- Sub PLO6.3 Research and develop yourself regularly
- Sub PLO6.4 Choose technology appropriately.
PLO-7 Demonstrate behavior that reflects morality, ethics, and public consciousness that is accepted by society.
- Sub PLO7.1 Demonstrate behavior that reflects responsibility towards oneself and society.
- Sub PLO7.2 Have morality, ethics, and academic ethics
- Sub PLO7.3 Work under the organization’s regulations
- Sub PLO7.4 Demonstrate volunteer and public consciousness behavior and act in a way that is valuable as a citizen of society.
Course Structure
Total credits studied throughout the course: 130 credits
| Courses |
Internship (credits) |
Cooperative (credits) |
| A. General education | 30 | 30 |
| 1) Languages subjects | 6 | 6 |
| 2) Humanities subjects | 8 | 8 |
| 3) Social sciences | 6 | 6 |
| 4) Sciences subjects | 6 | 6 |
| 5) Elective subjects | 4 | 4 |
| B. Specific courses | 94 | 94 |
| 1) Compulsory | 15 | 15 |
| 2) Core courses | 57 | 57 |
| 3) Elective courses | 22 | 22 |
| 4) Internship or Cooperative Education | Non-credit | Non-credit |
| C. Free elective courses | 6 | 6 |
| Total | 130 | 130 |
Study Plan
Admission Requirements
- Completion of high school in the science and mathematics study plan or an equivalent qualification is required.
- Successfully met the selection requirements set by the Office of the Higher Education Commission (OHEC) and/or the selection requirements of Prince of Songkla University, OR,
- Successfully met the selection requirements for the special project of the Faculty of Science and Technology, Prince of Songkla University, Pattani campus.
Graduation criteria
- Complete 130 credits according to the plan and pass the internship or cooperative education.
- Comply with the regulations of Prince of Songkla University on undergraduate studies and lifelong education, B.E. 2563, by completing the number of credits specified in the curriculum and receiving a grade point average of no less than 2.00 from an 8-point system.
- Participate in activities according to the regulations of Prince of Songkla University.
- Pass the English proficiency test results.
Teaching Management of the Program
Students can choose the study path according to their interests. The program has specified 4 study paths as follows:
Course details (TQF-2)
@ มคอ.2 หลักสูตรวิทยาศาสตรบัณฑิต สาขาวิชาคณิตศาสตร์และวิทยาการคอมพิวเตอร์ หลักสูตรปรับปรุง พศ. 2564
Download Documents / Manuals
@ คู่มือการศึกษาระดับปริญญาตรี สาขาวิชาคณิตศาสตร์และวิทยาการคอมพิวเตอร์ หลักสูตรปรับปรุง พศ. 2564
Program Executive Committee
- Asst. Prof. Saofee Busaman, Dr.rer.net (Algebra), University of Potsdam, Germany, 2007 รายละเอียดเพิ่มเติม
- Asst. Prof. Nifatamah Makaje, Doctoral Degree (Engineering Science), Johannes Kepler University Linz,
Austria, 2009 รายละเอียดเพิ่มเติม - Asst. Prof. Kittisak Tinpun, Dr.rer.net (Algebra), University of Potsdam, Germany, 2019 รายละเอียดเพิ่มเติม
- Asst. Prof. Nurin Dureh, Ph.D. (Research Methodology), Prince of Songkla University, Thailand, 2015 รายละเอียดเพิ่มเติม
- Miss Santhana Chaimontree, Ph.D. (Computer Science), University of Liverpool, U.K., 2012 รายละเอียดเพิ่มเติม
Contact information
Program Chair: Asst. Prof. Dr. Nurin Dureh
Email: nurin.d@psu.ac.th
Bachelor of Science (B.Sc.)
Applied Mathematics Program, 2017
B.Sc. (Applied Mathematics)
Philosophy of Education
Philosophy of University Education
Philosophy of the Program
The Bachelor of Science Program in Mathematics and Computer Science aims to produce graduates with knowledge in mathematics, statistics, and computer science, who can learn, develop themselves, and integrate their knowledge to solve problems or create innovations to develop organizations and society, as well as being virtuous and ethical.
The objectives of the curriculum
To organize teaching and learning to produce graduates with the following characteristics:
- To have knowledge and skills in mathematics, statistics, and computers.
- To have the ability to analyze problems using mathematics, reason, and apply them in various professional groups such as statistics, finance, insurance, and computers, in line with the development of human resources in science and technology and advanced studies.
- To have knowledge in research and be able to create innovations to develop organizations.
- To have morality, ethics in living in society, and professional ethics.
Highlights of the program
- The program offers teaching and learning that allows students to integrate knowledge in mathematics, statistics, and computer science.
- The program is equipped with modern tools and teaching methods.
- The faculty in the program has expertise in the field that is recognized both nationally and internationally.
Learning outcomes of the course (TQF)
Course Structure
Total credits throughout the course are not less than 133 credits.
Study Plan
Graduation criteria
- Complete 133 credits according to the plan and pass the internship or cooperative education.
- Comply with the regulations of Prince of Songkla University on undergraduate studies.
- Participate in activities according to the regulations of Prince of Songkla University.
Course Professor
- ผู้ช่วยศาสตราจารย์ ดร.เซาฟี บูสะมัญ, Dr.rer.net (Algebra), University of Potsdam, Germany, 2550 รายละเอียดเพิ่มเติม
- ผู้ช่วยศาสตราจารย์ ดร.นิฟาตมะห์ มะกาเจ, Doctoral Degree (Engineering Science), Johannes Kepler University Linz,
Austria, 2552 รายละเอียดเพิ่มเติม - ผู้ช่วยศาสตราจารย์ ดร.ทัดดาว ปานสมบัติ, Ph.D. (Computer Science), North Carolina State University, USA., 2554 รายละเอียดเพิ่มเติม
- ดร.นูริน ดือเร๊ะ, ปร.ด. (วิธีวิทยาการวิจัย), มหาวิทยาลัยสงขลานครินทร์, 2558 รายละเอียดเพิ่มเติม
- ดร.สันธนา ชัยมนตรี, Ph.D. (Computer Science), University of Liverpool, U.K., 2555 รายละเอียดเพิ่มเติม
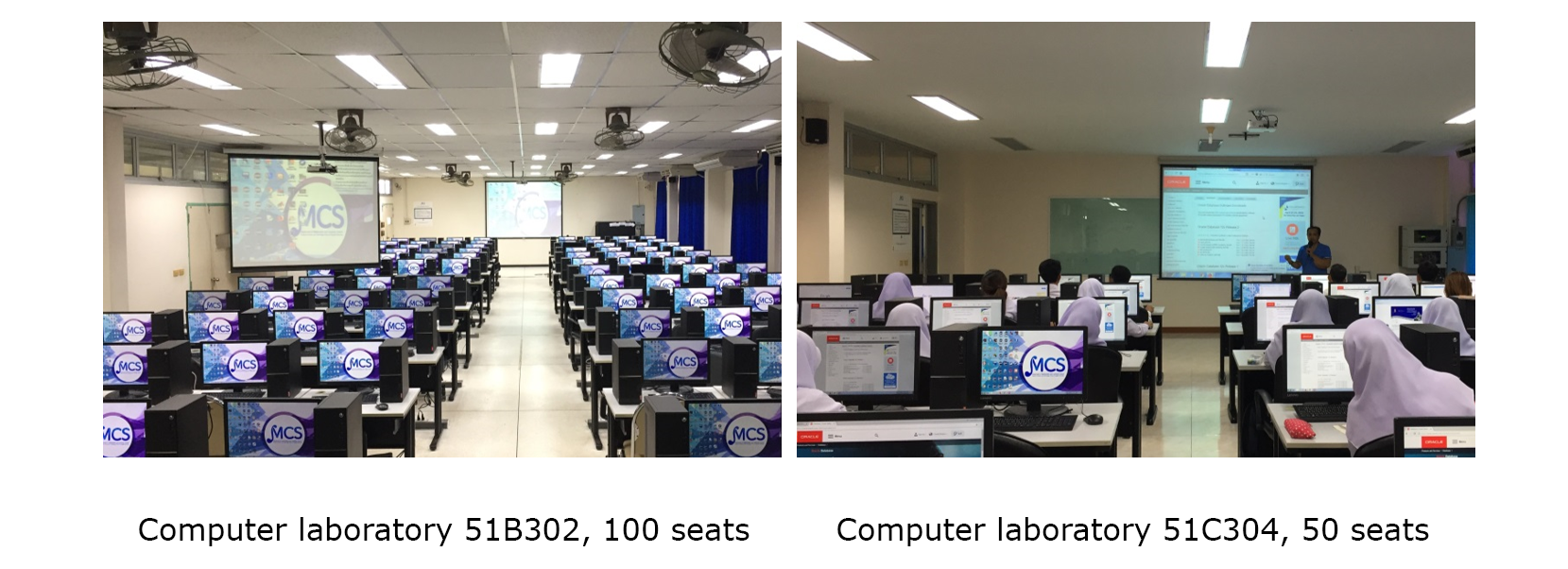
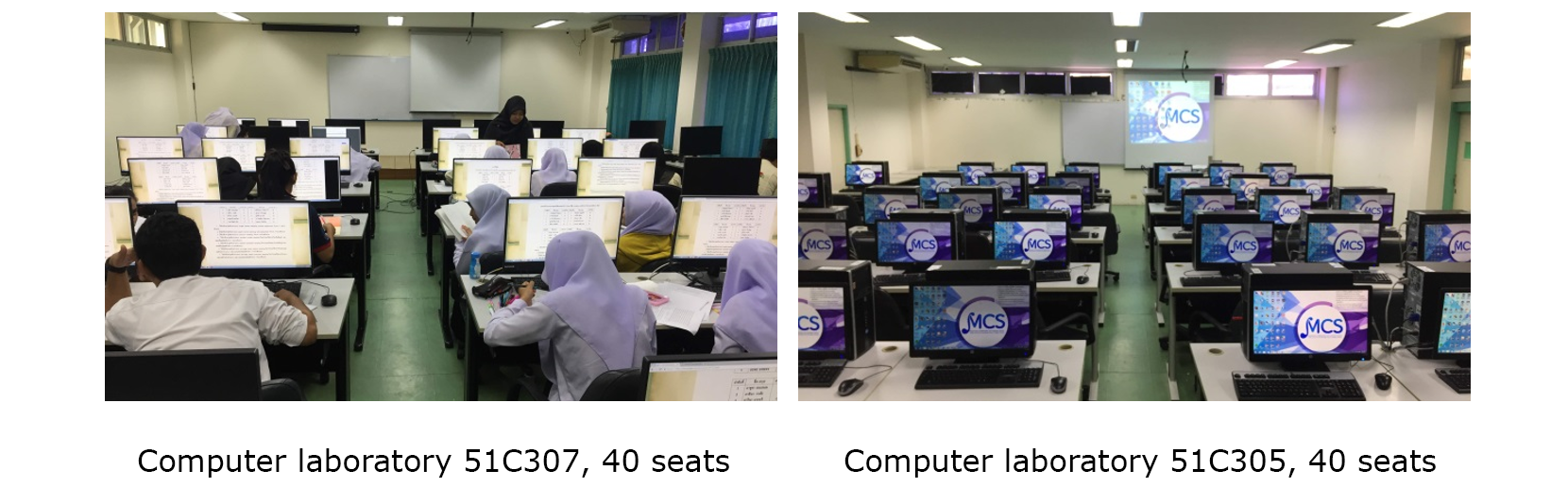
Facilities for teaching and learning
The program has 4 modern and adequate computer laboratories for students to practice mathematics, statistics, data science, and computer science, consisting of:
- 1 x 100-seat computer lab
- 1 x 50-seat computer lab
- 2 x 40-seat computer labs


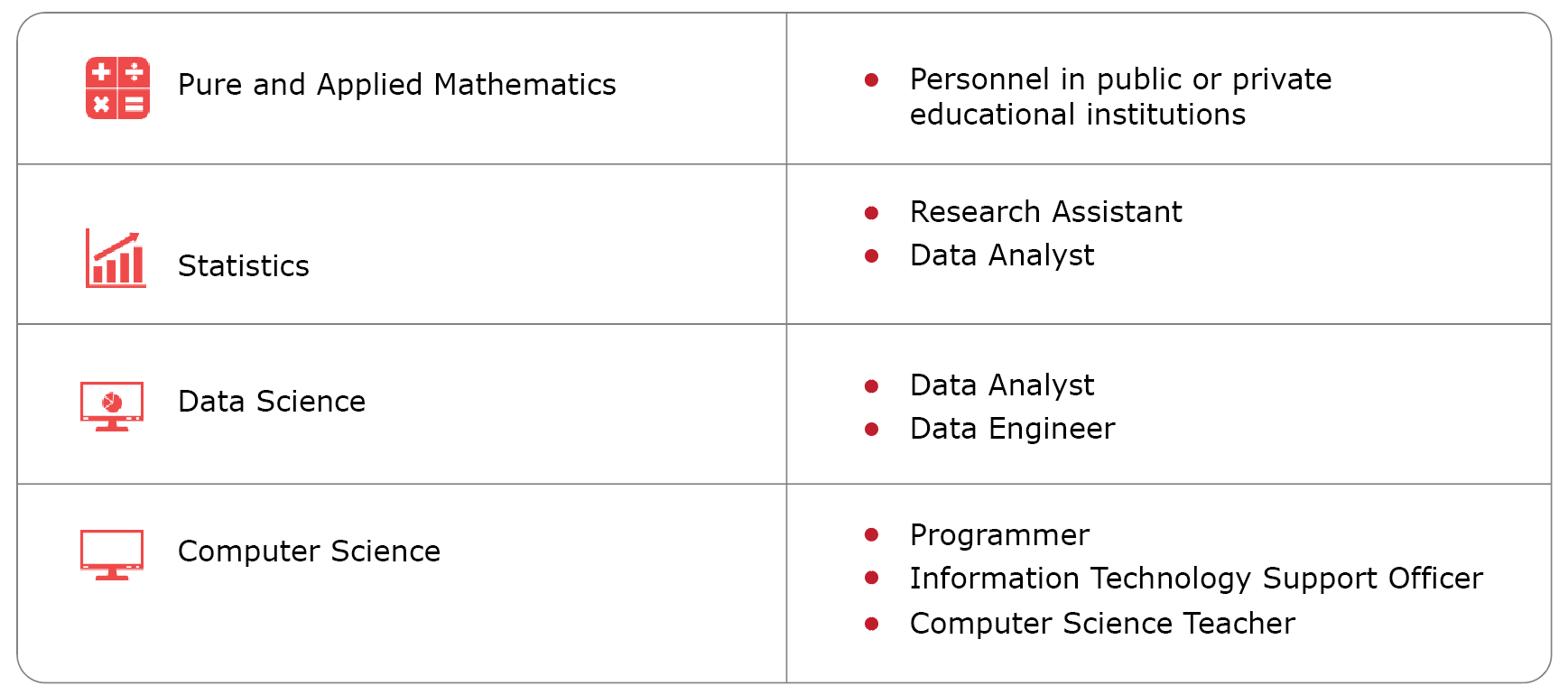
Career Path
Able to work in organizations or agencies in both the public and private sectors, in education or academics, life insurance system analysis, insurance, finance and banking, research related to mathematics, statistics, and computer science, and a freelance career

Why study applied mathematics and computer science?
Everything around us involves “mathematics.” Mathematicians are thinkers, analysts, forecasters, and planners. Examples of what students will develop their potential when studying Applied Mathematics at the Faculty of Science and Technology, Prince of Songkla University (depending on specific interests) :
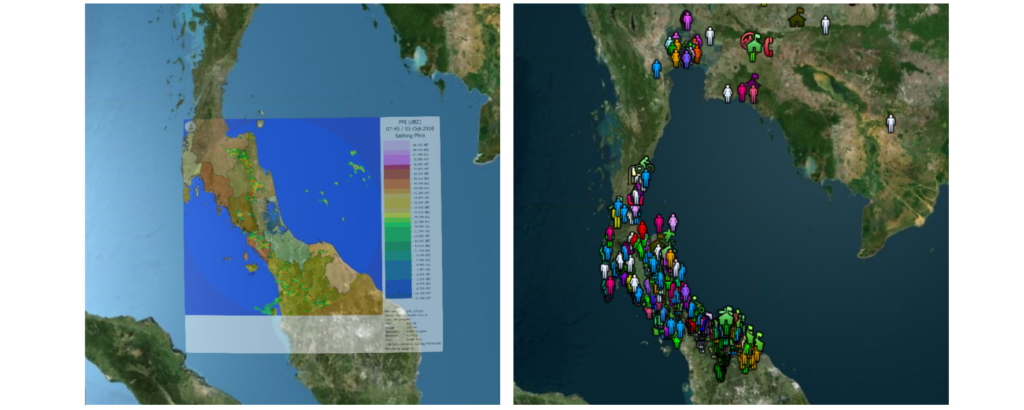
Mathematics and weather forecasting and natural disaster monitoring
Forecasting future events or phenomena requires the application of mathematical and statistical data and knowledge to analyze possible trends in order to predict phenomena that may occur in the future. For example, weather forecasting requires statistical data and reading aerial photographs and using knowledge of computer science to develop programs for spatial display.
Mathematics and Computer Science and Information Technology
Mathematics is the foundation of computer science and information science, which collects and analyzes data. It requires computers to help in thinking and calculating, resulting in data in various forms, including numbers, letters, sounds, still images, and motion pictures. Computer science is a direct result of mathematics. All current career fields require the use of computers.
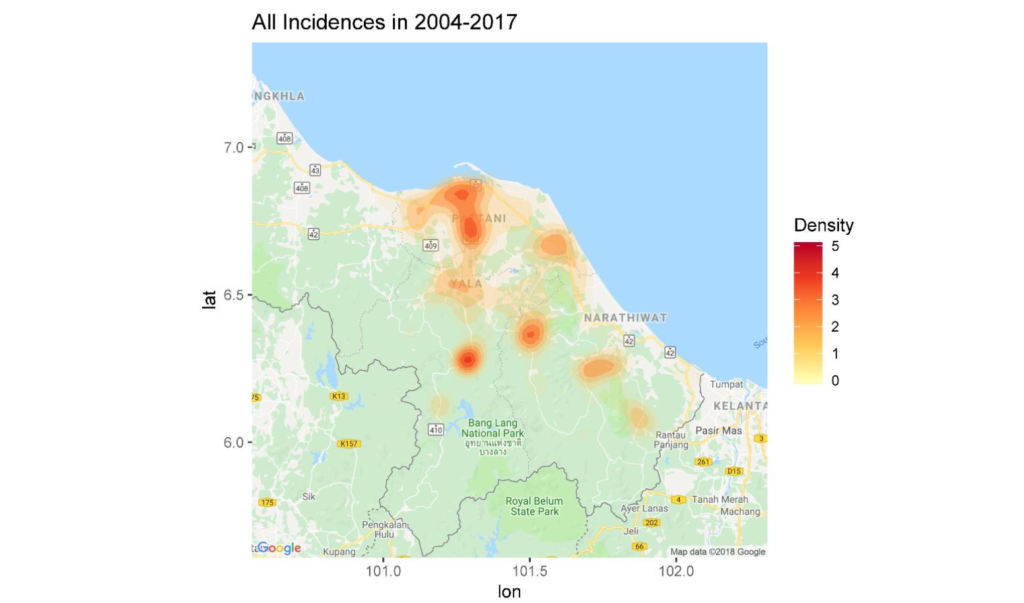
Mathematics and statistical modeling and data visualization
Mathematics leads to statistical modeling and data science, which involves data collection, data management, modeling or simulation to predict or explain various phenomena of data for decision-making, and designing and displaying data in various formats to present such data, such as graphs, spatial displays, etc.
Mathematics and Architecture and Engineering
Architecture and engineering require mathematical knowledge to help design buildings, such as measuring light, humidity, and shade; calculating angles of various parts; and helping to make construction more accurate. Calculating weight bearing, helping to make the building more stable. Calculating the use of construction materials and equipment, helping to estimate construction costs, etc.